潍坊北部晚第四纪介形类与环境演变研究
【类型】期刊
【作者】李守军,陈宇慧,赵秀丽,王丽丽,崔肖辉,刘强,刘晓(山东科技大学地球科学与工程学院)
【作者单位】山东科技大学地球科学与工程学院
【刊名】山东科技大学学报(自然科学版)
【关键词】 介形类;海侵;晚第四纪;潍坊北部;环境演变
【资助项】山东科技大学研究生科技创新基金项目
【ISSN号】1672-3767
【页码】P1-11
【年份】2019
【期号】第1期
【期刊卷】4;|5;|2
【摘要】盐度、温度等环境变化对介形类的属种组合、丰度、分异度等起着重要的控制作用。通过对莱州湾南岸地区潍坊北部的GK59孔、GK74孔、GK79孔、GK89孔的介形类样本的实验处理和分析,对以Neomonoceratina delicate,Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Pistocythereis bradyformis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa为优势的海相介形类和以Candoniella albicans,Candoniella pellucida,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Ilyocypris subpulchra为优势的淡水介形类进行划分,并与周边已知钻孔进行对比,认为此区域共发育三个海侵层,第Ⅲ海侵层和第Ⅱ海侵层发生在晚更新世,分别对应晚沾化海侵和献县海侵,第Ⅰ海侵层发生在全新世,对应黄骅海侵。并总结晚更新世以来的沉积层序和海侵范围,阐明研究区的沉积环境演化历史。
【全文】 文献传递
潍坊北部晚第四纪介形类与环境演变研究
摘 要:盐度、温度等环境变化对介形类的属种组合、丰度、分异度等起着重要的控制作用。通过对莱州湾南岸地区潍坊北部的GK59孔、GK74孔、GK79孔、GK89孔的介形类样本的实验处理和分析,对以Neomonoceratina delicate,Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Pistocythereis bradyformis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa为优势的海相介形类和以Candoniella albicans,Candoniella pellucida,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Ilyocypris subpulchra为优势的淡水介形类进行划分,并与周边已知钻孔进行对比,认为此区域共发育三个海侵层,第Ⅲ海侵层和第Ⅱ海侵层发生在晚更新世,分别对应晚沾化海侵和献县海侵,第Ⅰ海侵层发生在全新世,对应黄骅海侵。并总结晚更新世以来的沉积层序和海侵范围,阐明研究区的沉积环境演化历史。
关键词:介形类;海侵;晚第四纪;潍坊北部;环境演变
晚第四纪以来,我国渤海地区经历了多次海陆变迁,以发育海陆交互相与三角洲相为主要特点,形成了海相沉积物和陆相沉积物交替出现的地层[1]。前人研究表明,自晚更新世以来,莱州湾南岸以间歇性持续沉降为主,海平面发生过多次重大变化,受多次海侵影响。由于介形类的古生态学可以提供重要的环境变化信息[2],对介形类属种组合及分布特征的分析,可以更准确地得出莱州湾地区海侵的环境变化时期及受海侵影响的范围。本研究以潍坊北部GK59孔、GK74孔、GK79孔和GK89孔的陆地岩芯为基础,根据岩性特征、介形类的属种组合等,分析潍坊北部地区晚更新世以来的沉积环境变化,并结合前人已探明的资料还原沉积环境演化历史。
1 研究材料与鉴定结果
1.1 研究材料及方法
样品取自莱州湾南岸地区潍坊北部GK59孔、GK74孔、GK79孔、GK89孔(图1),共提取岩芯沉积物样品192个,样品采用标准的微体化石分析方法进行处理。先将样品放入50 ℃的烘箱进行干燥,称取样品各150 g,泡入清水中静置三天,分散不好的可滴入少量5%的双氧水[3],待样品充分分解后,用200目和100目的网筛自下到上套叠,进行筛样。分别收集两个粒级网筛中的剩余样品并进行低温烘干。将200目和100目的筛网中的样品分别收集待用,在显微镜下挑选出所得的介形类样品进行微体古生物鉴定[4-11]和数量统计。
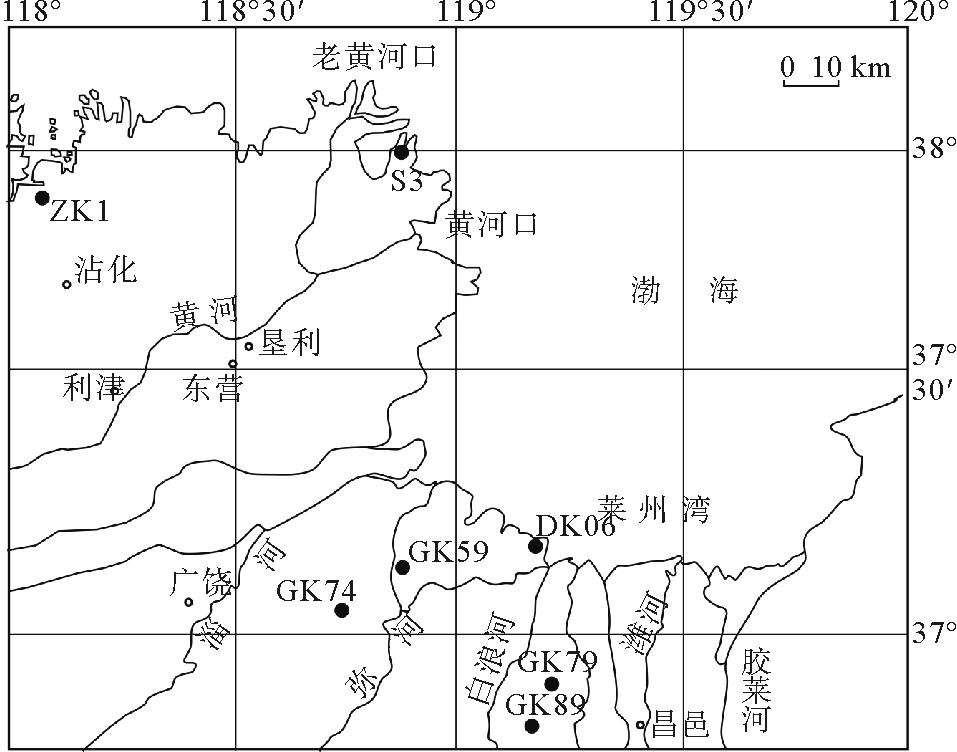
图1 研究区与钻孔位置
Fig.1 Map of study area and core locations
1.2 鉴定结果
经鉴定,在86个样品中得到了介形类化石,包含21个科,50个属,87个种。其中,海相介形类属种占优势(图版I),主要有近日本海花介Sinopontocythere subjaponica(图版I(1)),腹结细花介Leptocythere ventriclivosa(图版I(5)),苏门答腊奇美花介Perissocytheridea sumatrensis(图版I(6)),东台新单角介Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis(图版I(8)),欢乐新单角介Neomonoceratina delicate(图版I(9)),舟耳形介Aurila cymba(图版I(10)),矩形新中华花介Neosinocythere elongata(图版I(11)),布氏纯艳花介Pistocytheteis bradyi(图版I(13)),布氏形纯艳花介Pistocytheteis Bradyformis(图版I(14)),网纹半美花介Hemicytheridea reticulata(图版I(15)),大海花介Pontocythere spatiosus等。其中,见少量代表水体较深的介形类化石,眼点弯贝介Loxoconcha ocellata(图版I(3)),滨海弯贝介Loxoconcha binhaiensis(图版I(4)),中国花花介Callistocythere sinensis(图版I(2)),三角形中华海花介Sinopontocythere triangulata(图版I(7)),网纹豆艳花介Leguminocythreis reticulata(图版I(12)),日本穆赛介Munseyella japonica,皱新单角介Neomonoceratina crispata,英勇戳花介Stigmatocythere bona,这些种主要分布在水深20~50 m的浅水区。
鉴定出的淡水介形类化石也较多(图版II),主要有斯氏达尔文介Darwinula steveasoni(图版II(1)),苏氏小玻璃介Candoniella cf.suzini(图版II(2)),平滑玻璃介Candona levis(图版II(3)),高邮土星介Ilyocypris gaoyouensis(图版II(4)),近美丽土星介Ilyocypris subpulchra(图版II(5)),近布氏土星介Ilyocypris subbradyi(图版II(6)),粗糙土星介Ilyocypris salebrosa(图版II(7)),透明小玻璃介Candoniella pellucida(图版II(8)),纯净小玻璃介Candoniella albicans(图版II(9)),压缩玻璃介Candona compressa(图版II(10)),圣贵湖花介Limnocythere sanctipatricci(图版II(12)),网纹湖花介Limnocythere dectyophora,弯脊湖花介Limnocythere sinucostata,光滑湖花介Limnocythere luculenta,背隆湖花介Limnocythere dorsiconvexa,刺土星介Ilyocypris spinosa等。
鉴定出的广盐类介形类化石(图版II),其中压印中华美花介Sinocytheridea impressa(图版II(13))含量最多,广泛分布于我国的近海沿岸地区。还有古屋刺面介Spinileberis furuyaensis(图版II(11)),美山双角花介Bicornucythere bisanensis(图版II(14))。
2 介形类化石组合特征及其沉积环境分析
自晚更新世以来,潍坊北部莱州湾沿岸受多次海侵的影响,海陆相地层交替叠置的现象十分明显。通过上述四个钻孔的岩性特征、介形类化石含量及组合特征等进行分析,识别出其存在的沉积环境(图2)。
2.1 GK59孔介形组合特征及其沉积环境
对40个样品进行了古生物鉴定,其中19个样品中发现介形类化石,主要分布在孔深0.8~10.4 m,15.3~33.7 m和53.8~55 m,含10个科,20个属,38个种,共受三次海侵影响。
孔深0~8.3 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粉砂质粘土,含少量钙质结核和铁质锈染,含海相贝壳碎片,介形类Ilyocypris subbradyi,I.subpulchra,I.gaoyouensis,Limnocythere luculenta,L.postinodosa,Sinocytheridea impressa,共3属6种,介形类丰度为18瓣/g,主要为淡水介形类,仅有少量海相分子。该组合代表以陆相为主的海陆交互相沉积[12-13]。
孔深8.3~15.7 m,地层岩性为浊黄色粉砂质粘土,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,其中9.41 m处可见近垂向生物潜穴,介形类Sinocytheridea impressa,Sinopontocythere subjaponica,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Candoniella albicans,共5属5种,本层介形类以海相介形类为主,丰度和分异度都很小,介形类丰度为3瓣/g,个别层位出现少量淡水介形类化石。该组合代表以海相为主的海陆交互相沉积环境。
孔深15.7~20.5 m,地层岩性以棕黄色粉砂为主,可见海相贝壳碎片,发育水平层理,介形类Neomonoceratina crispata,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Callistocythere sinensis,Neomonoceratina delicate,N.dongtaiensis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Pistocytheteis bradyi,Sinopontocythere subjaponica,Sinocytheridea impressa,Bicornucythere bisanensis等,共10属19种。本层介形类丰度和分异度最为丰富,优势种为海相介形类,在孔深19.3 m出现峰值,丰度达166枚/g,主要为海相介形类组成,并有大量的有孔虫化石。组合中以Loxoconcha binhaiensis(30%),Bicornucythere bisanensis(16%),Sinocytheridea impressa(11.5%)为优势种,其他主要分子有Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Neomonoceratina delicate。该组合特征代表滨海-浅海相的沉积环境[14]。
孔深20.5~23 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粘土质粉砂,可见铁质锈染,生物潜穴,偶见海相贝壳碎片,介形类Pistocytheteis Bradyformis,Perissocytheridea sumatrensis,Sinocytheridea impressa,Bicornucythere bisanensis,Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Pistocytheteis bradyi,共6属8种,介形类的丰度和分异度都明显减少,平均9瓣/g样品,以Bicornucythere bisanensis(44.6%)为优势种,Sinocytheridea impressa(17.1%),该组合代表河口至滨岸沉积环境[15-16]。
孔深23~28.9 m,地层岩性以棕黄色粉砂为主,可见细砂条带和铁质锈染,发育水平层理,可见海相贝壳碎片,介形类Neomonoceratina delicate,N.dongtaiensis,Pistocytheteis Bradyformis,Pistocytheteis bradyi,Sinopontocythere subjaponica,Perissocytheridea sumatrensis,Neosinocythere elongata,Leguminocythreis reticulata,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Callistocythere sinensis,Sinocytheridea impressa,Bicornucythere bisanensis等,共9属15种。本层介形类丰度和分异度明显增加,平均61瓣/g样品,主要由海相介形类组成,并有大量的有孔虫化石。组合中以Loxoconcha binhaiensis(25%),Bicornucythere bisanensis(9.7%),Sinocytheridea impressa(6%)为优势种,其他主要分子有Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Neomonoceratina delicate。该组合代表滨海-浅海相的沉积环境。
孔深28.9~32 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粘土质粉砂,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,海相贝壳碎片,介形类Sinocytheridea impressa,Bicornucythere bisanensis,Pistocytheteis bradyi,Candoniella albicans,Ilyocypris subbradyi,共5属5种,本层介形类丰度和分异度明显降低,丰度为12瓣/g,该组合代表以海相为主的海陆交互相沉积环境[17-18]。
孔深32~42 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粘土,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,淡水螺壳碎片,介形类Candoniella albicans,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Sinocytheridea impressa,共3属3种,本层介形类化石含量低,仅有零星分布,该组合代表以陆相为主的海陆交互相沉积环境。
孔深42~47.6 m,地层岩性为浊棕黄色粉砂质粘土,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,淡水螺壳碎片,多处发育有机质条带,介形类Bicornucythere bisanensis,Pistocytheteis bradyi,Sinocytheridea impressa,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Sinocytheridea impressa,共5属5种,该组合代表以海相为主的海交互相沉积环境。
孔深47.6~54.5 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粉砂,可见细砂条带和铁质锈染,发育水平层理,可见海相贝壳碎片和生物潜穴,介形类Leguminocythreis reticulata,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Sinocytheridea impressa,Bicornucythere bisanensis,Stigmatocythere bona,Aurila miii,共6属9种。本层介形类丰度和分异度增加,平均21瓣/g样品,主要由海相介形类组成。该组合代表滨海-浅海相沉积环境。
孔深54.5~60 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粘土质粉砂,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,虫孔、根孔较发育,见淡水螺壳碎片,介形类Candoniella albicans,C.pellucida,共1属2种,本层仅含有极少量介形类化石,该组合代表陆相沉积环境(图2(a))。
2.2 GK74孔沉积环境分析
对50个样品进行了古生物鉴定,其中17个样品中发现介形类化石,主要分布在孔深6.0~7.9 m,15.3~22.5 m和35.4~55.3 m,含11个科,19个属,31个种,受两次海侵影响。
孔深15~18.7 m,地层岩性为棕黄色含粘土粉砂岩,偶见海相贝壳碎片,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,丰度达到最高,平均67瓣/g,以Sinocytheridea impressa(17.9%),Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis(12.1%),Sinopontocythere subjaponica(9.5%)为优势种,其中还包括Bicornucythere bisanensis,Pistocytheteis bradyformis,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leguminocythreis reticulata,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Candoniella albicans,代表滨海-浅海相沉积环境。
孔深21.4~24.5 m,地层岩性为棕黄色粘土质粉砂,可见钙质结核和铁质锈染,介形类以Sinocytheridea impressa(22.7%),Loxoconcha binhaiensis(17.4%),Sinopontocythere subjaponica(9.5%)为优势种,其中还包括Bicornucythere bisanensis, Sinocytheridea longa,代表滨海-浅海相沉积环境(图2(b))。
2.3 GK79孔沉积环境分析
对54个样品进行了古生物鉴定,其中36个样品中发现介形类化石,主要分布在孔深2.7~26.23 m,29.4~34.3 m和43~54.5 m,含18个科,31个属,51个种,共受三次海侵影响。
孔深9.5~14 m,地层岩性为灰黄色粉砂,见水平层理,含海相贝壳碎片,丰度达到最高,平均95瓣/g,以Bicornucythere bisanensis(32.6%),Loxoconcha binhaiensis(17.2%),Sinocytheridea impressa(9.5%)为优势种,还含有Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Sinopontocythere subjaponica,Pistocytheteis bradyformis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leguminocythreis reticulata,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Candoniella albicans,Candona compressa,Darwinula fustiformis,该组合代表滨海-浅海相沉积环境。
孔深20.2~24.9 m,地层岩性为浊黄棕色含粘土粉砂层,见水平层理,含海相贝壳碎片,平均49瓣/g,以Loxoconcha binhaiensis(29.2%),Sinocytheridea impressa(22.5%),Perissocytheridea sumatrensis(13.4%)为优势种,还含有Sinopontocythere subjaponica,S.triangulata,Pistocytheteis bradyformis,Callistocythere sinensis,Leguminocythreis reticulata,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Candoniella albicans,该组合代表滨海-浅海相的沉积环境。
孔深43~44.3 m,地层岩性为橙色含粘土粉砂层,可见网纹状铁质结核和近垂向生物潜穴,平均28瓣/g,以Sinocytheridea impressa(27.5%),Loxoconcha binhaiensis(19.1%)为优势种,还含有Loxoconcha ocellata,Hemicytheridea reticulata,Pistocytheteis bradyformis,Leguminocythreis reticulata,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Ilyocypris subbradyi,Candoniella albicans,该组合代表滨海-浅海相沉积环境(图2(c))。
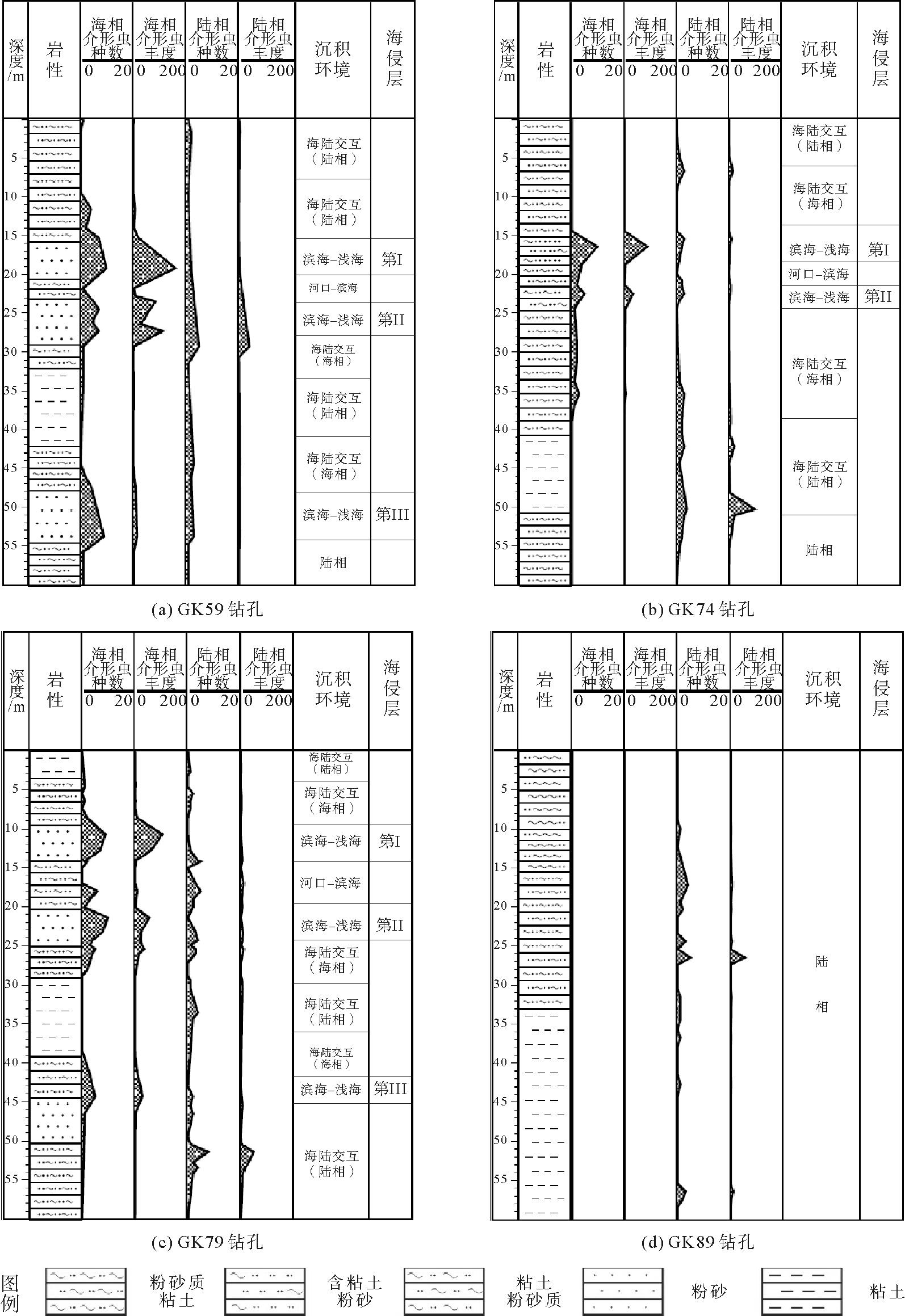
图2 各钻孔柱状图及沉积环境分析
Fig.2 General sedimentary environment evolution of each core
2.4 GK89孔沉积环境分析
共对48个样品进行了古生物鉴定,其中14个样品中发现介形类化石,主要分布在孔深10~26.6 m,31.5~42.8 m和56.4~57.9 m,含7个科,11个属,19个种。经鉴定,均为淡水介形类,说明此孔未受海侵影响(图2(d))。
3 环境演化历史
莱州湾沿岸第四纪钻孔虽多,但测年资料不多。选取黄河三角洲区域的钻孔S3,ZK1,并参考研究区已有C14测年数据的钻孔DK06,可以看出几个参考孔与研究孔的地层序列基本一致。将几个参考孔的C14测年数据与本区四个钻孔进行对比,可以推测三个海侵层位对应的年代,并总结研究区晚更新世以来的海侵范围(图3)。
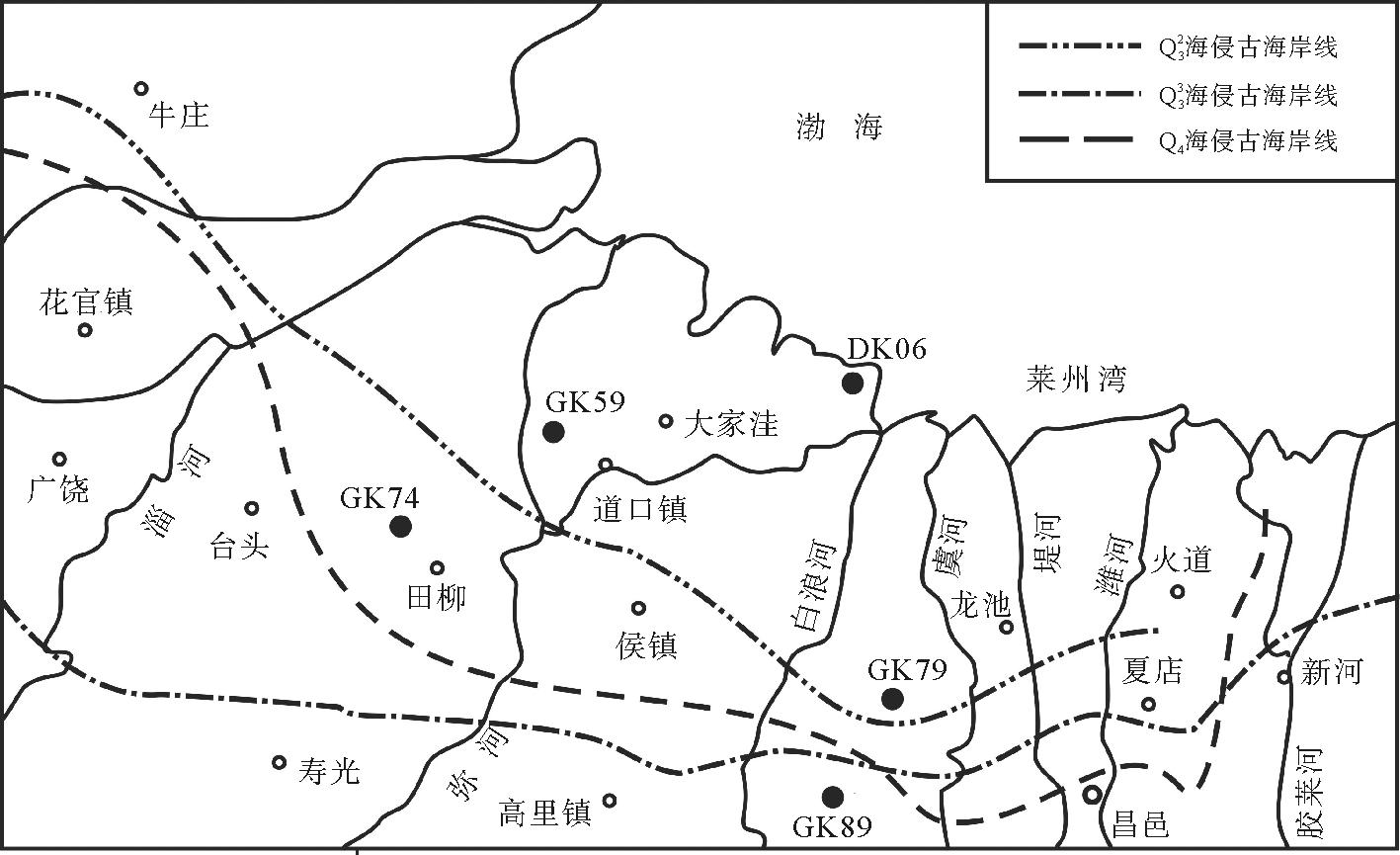
图3 潍坊北部古海岸线位置图
Fig.3 Scope of marine transgression and coastline change
大约在距今34 ka开始,气候变暖,全球海平面上升,沉积了研究区的第III海侵层,介形类以海相为主,包括Leguminocythreis reticulata,Sinocytheridea impressa,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Bicornucythere bisanensis,Stigmatocythere bona等。第三海侵层代表了晚更新世中期的海侵事件,对应晚沾化海侵,此海侵层仅见于GK79以及GK59的钻孔中,而在GK74及GK89中没有出现,古海岸线大致位于花官镇北部,向东延伸到田柳镇南部,昌邑至夏店附近。随后气候变冷,海水再次退出胶州湾,使渤海裸露成平原[19-22]。
大约在距今28 ka开始,气候再次变暖,全球海平面上升,淹没了渤海,沉积了本研究区的第II海侵层,其中含有大量的海相介形类化石,有Bicornucythere bisanensis,Sinocytheridea impressa,Pontocythere spatiosus,Loxoconcha binhaiensis,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Neomonoceratina delicate,Perissocytheridea sumatrensis,Neosinocythere elongata,Leguminocythreis reticulata等。第Ⅱ海侵层代表了晚更新世晚期的海侵事件,对应献县海侵,此海侵层见于GK59,GK74以及GK79的钻孔中,古海岸线大致位于广饶南部,向东一直延伸到寿光和昌邑北侧,至新河附近。之后气候变冷,海平面下降,海水退出本区。
大约距今8 ka开始,气候急剧升温,海水淹没本区,沉积了本区的第I海侵层,含海相介形类化石丰富,其中有Loxoconcha binhaiensis,L.ocellata,Neomonoceratina crispata,Callistocythere sinensis,Neomonoceratina delicate,N.dongtaiensis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa,Pistocytheteis bradyi,Sinopontocythere subjaponica等,对应黄骅海侵。第Ⅰ海侵层代表了全新世海侵的影响范围,古海岸线大致分布于台头镇、侯镇、昌邑、夏店及火道一带。本研究区保存有古黄土海蚀崖,为本时期的古海岸遗迹[23]。
4 结论
1)通过对潍坊北部GK59孔,GK74孔,GK79孔,GK89孔沉积物中所含的介形类鉴定分析,海相种与陆相种的介形类属种差异十分明显。海相种以Neomonoceratina delicate,N.dongtaiensis,Pistocytheteis bradyformis,Pontocythere spatiosus,Leptocythere ventriclivosa为优势种,其中还含有代表水体较深的Leguminocythreis reticulata,Munseyella japonica。淡水种以Candoniella albicans,Candona compressa,Candona levis,Ilyocypris subbradyi,I.subpulchra为优势种。
2)晚更新世以来,潍坊北部地区可识别出三个海侵层及古海岸线分布,第Ⅲ海侵层和第Ⅱ海侵层发生在晚更新世,分别对应晚沾化海侵和献县海侵,第Ⅰ海侵层发生在全新世,对应黄骅海侵。本区域与周边区域互相结合,丰富了晚更新世以来莱州湾地区沉积环境演化和海平面变化的研究。
参考文献:
[1]胥勤勉,袁桂邦,张金起,等.渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J].地质学报,2011,85(8):1352-1367.
XU Qinmian,YUAN Guibang,ZHANG Jinqi,et al.Stratigraphic division of the late Quaternary strata along the coast of Bohai bay and its geology significance[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2011,85(8):1352-1367.
[2]李军,余俊清.湖相介形虫古生态学在环境变化研究中的应用[J].盐湖研究,2002,10(1):66-71.
LI Jun,YU Junqing.Application of lacustrine ostracodes to the study of environmental changes[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2002,10(1):66-71.
[3]张家武,何晶,陈硕,等.第四纪湖相介形虫类壳体化石在古环境中的应用[J].地球科学进展,2009,24(11):1229-1237.
ZHANG Jiawu,HE Jing,CHEN Shuo,et al.Applications of non-marine ostracods in Quaternary paleoenvironment ent-advances and problems in fossil assemblages[J].Advances in Earth Science,2009,24(11):1229-1237.
[4]侯祐堂,勾韵娴,陈德琼,等.中国介形类化石:第一卷[M].北京:科学出版社,2002:135-142.
[5]侯祐堂,勾韵娴,陈德琼,等.中国介形类化石:第二卷[M].北京:科学出版社,2007:256-275.
[6]陈德琼,杨怀仁,周全春,等.江苏地区白垩纪:第四纪介形类动物群[M].北京:地质出版社,1982:59-71.
[7]汪品先,章纪军,赵泉鸿,等.东海底质中的有孔虫和介形虫[M].北京:海洋出版社,1988:64-69.
[8]BLANCE M,JULIO R.The “northern guests” and other palaeoclimatic ostracod proxies in the late Quaternary of the Basque Basin[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2015,419(7):100-114.
[9]GLIOZZI E,GROSSI F.Late Messinian lago-mare ostracod palaeoecology:A correspondence analysis approach[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2008,264(3):288-295.
[10]FRENZEL P,IAN B.The use of ostracods from marginal marine,brackish waters as bioindicators of modern and Quaternary environmental change[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2005,225(5):68-92.
[11]SUN Zhencheng,FENG Xiaojie.Ostracoda and palaeoenvironments of the northeastern Tarim Basin,western China[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,1999,148(11):37-50.
[12]赵泉鸿,汪品先,张清兰.南海北部陆架底质中介形虫的分布[J].海洋学报.1986,8(5):590-602.
ZHAO Quanhong,WANG Pinxian,ZHANG Qinglan.Ostraoda distribution in the north shelf bottom of South Sea[J].Acta of Oceanoloogica Sinica,1986,8(5):590-602.
[13]PENG P,ZHU L,FRENZEL P,et al.Water depth related ostracod distribution in lake Pumoyum Co,southern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary International,2013,313(8):47-55.
[14]庄振业,许卫东,刘东生,等.渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,1999,19(2):27-35.
ZHUANG Zhenye,XU Weidong,LIU Dongsheng,et al.Division and environmental evolution of late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai sea[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology,1999,19(2):27-35.
[15]刘升发,庄振业,吕海青,等.埕岛及现代黄河三角洲海域晚第四纪地层与环境演变[J].海洋湖沼通报,2006(4):32-37.
LIU Shengfa,ZHUANG Zhenye,LÜ Haiqing,et al.The strata and environmental evolution in the late Quaternary in the Chengdao area and modern Yellow River delt coast[J].Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology,2006(4):32-37.
[16]林防,王建中,李建芬,等.渤海莱州湾第四纪晚期以来微体化石组合特征和沉积环境演化[J].地质通报,2005,24(9):879-884.
LIN Fang,WANG Jianzhong,LI Jianfen,et al.Characteristics of microfossil assemblages and evolution of the sedimentary environment since the late Quaternary in the Laizhou Bay,Bohai Sea[J].Geological Bulletin of China,2005,24(9):879-884.
[17]LIU J G,LI A C,CHEN M H.Environmental evolution and impact of the Yellow River sedimentson deposition in the Bohai Sea during the last deglaciation[J].Asian Earth Sciences,2010,38(1):26-33.
[18]李国刚,胡邦琦,毕建强,等.黄河三角洲ZK1孔晚第四纪以来沉积层序演化及其古环境意义[J].沉积学报,2013,31(6):1050-1058.
LI Guogang,HU Bangqi,BI Jianqiang,et al.Stratigraphic evolution of the Huanghe delta(Bohai Sea)since the late Quaternary and its paleoenvironmental implications:Evidence from core ZK1[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2013,31(6):1050-1058.
[19]林防,李凤林,李建芬,等.渤海湾西北岸全新世介形类组合特征及海进海退旋回[J].地球学报,2004,25(1):53-58.
LIN Fang,LI Fenglin,LI Jianfen,et al.Holocene ostracoda assemblages and marine transgression-regression cycle in the northwestern coastal area of the Bohai gulf[J].Acta Geoscientia Sinica,2004,25(1):53-58.
[20]杨怀仁,陈西庆.中国东部第四纪海面升降、海侵海退与岸线变迁[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,1985,5(4):59-80.
YANG Huairen,CHEN Xiqing.Quaternary transgressions,eustatic changes and shifting of shoreline in east China[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology,1985,5(4):59-80.
[21]王强.渤海湾西岸第四纪海相及海陆过渡相介形虫化石群及古地理[J].海洋地质研究,1982,2(3):36-46.
WANG Qiang.The ostracod fauna of marine and marineterrestrial transitional facies in western coast of the Bohai gulf(north China)and paleogeography during Quaternary[J].Marine Geological Research,1982,2(3):36-46.
[22]韩有松,孟广兰,王少青.渤海莱州湾滨海平原晚第四纪地质事件与古环境[J].海洋科学集刊,1994,35(10):87-96.
HAN Yousong,MENG Guanglan,WANG Shaoqing.The geological events and paleo-environment of the coastal plain of Laizhou Bay in Bohai sea during late Quaternary[J].Studia Marina Sinica,1994,35(10):87-96.
[23]杨怀仁,王建.黄河三角洲地区第四纪海进与岸线变迁[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,1990,10(3):1-14.
YANG Huairen,WANG Jian.Quaternary transgressions and coastline changes in Huanghe River delta[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology,1990,10(3):1-14.
(责任编辑:高丽华)
Late Quaternary Ostracoda and Environmental Evolution in the North Weifang
Abstract:Environmental evolution such as changes in salinity and temperature plays an important role in controlling the taxa,diversity and abundance of Ostracoda.By experimental treatment and analysis of the ostracod samples from the Cores of GK59,GK74,GK79,GK89 in the south coast of Laizhou bay,north of Weifang,this paper divided Ostracoda into marine Ostracoda,which took Neomonoceratina delicate,Neomonoceratina dongtaiensis,Pistocythereis bradyformis,Pontocythere spatiosu,and Leptocythere ventriclivosa as the advantages,and fresh water ostracoda,which took Candoniella albicans,Candoniella pellucida,Ilyocypris subbradyi,and Ilyocypris subpulchra as the advantages.After they were compared with Ostracoda in the known surrounding cores,it was concluded that this area had developed three transgression layers.The third and the second layer transgression happened in the late Pleistocene,corresponding to the late Zhanhua transgression and Xianxian transgression respectively,while the first layer transgression happened in the Holocene,corresponding to the Huanghua transgression.The scope of transgression and sedimentary sequence since the late Pleistocene were summarized and the evolution of sedimentary environment of this area was clarified.
Key words:Ostracoda;marine transgression;late Quaternary;North Weifang;environmental evolution
收稿日期:2015-11-05
基金项目:山东科技大学研究生科技创新基金项目(YC150320)
中图分类号:P52
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-3767(2016)01-0001-11
